오버라이드 / 동적바인딩
저번시간 짧게 복습..
<캡슐들을 서로 사용하는 관계들 종류>
1. 그냥 사용
2. has a : 부품을 가져와서 조립하는것 (포함관계)
3. is a : 부품이 아닌 틀(프레임워크) 을 가져와서 수정하고 확장하는것
ㄴ 틀이 딱 내가 원하는 캡슐이라면 틀로 사용하지 않음. 그러니 틀을 사용하는 캡슐은 그 틀을 확장?하거나 고쳐서?사용하는것이다
- 보통 has a 상속은 상속이라고 표현하지 않는다
- 오버라이드: 가리다,덮어쓰기,재정의하기
- 오버라이드를 하게되면 오버라이드 메소드가 부모 메소드를 가린다
- 오버라이드와 오버로드는 완전 다른것
- 오버라이드를 하게 되면 부모를 가리기 때문에 호출할때도 부모가 갖고있는 인자를 직접 호출하지 못하고, 함수롤 통해 호출이 가능하다
ex) 부모가 kor를 갖고 있고 getKor함수를 만들었다면, 오버라이드한거는 kor를 직접 못부르고 getKor함수를 불러야한다
- 부모,자식 클래스 (extens 00 하면 이쪽이 부모)
public NewlecExam() {
this(10,10,10,10); //아래 매개변수들을 10,10,10,10으로 초기화
}
public NewlecExam(int kor,int eng,int math,int com) {
setKor(kor);
setEng(eng);
setMath(math);
//상속 받은것
this.com = com;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
NewlecExam exam = new NewlecExam();
System.out.println(exam.total());
//오버라이드된 total이 출력
- 부모를 가지는 클래스는 두 개의 객체를 생성한다
- new( ) 할때는 메서드가 올라가는건 아니다
- super : 부모의 객체를 의미할때 붙인다

- super를 붙이면 부모의 인자들을 불러올수 있다
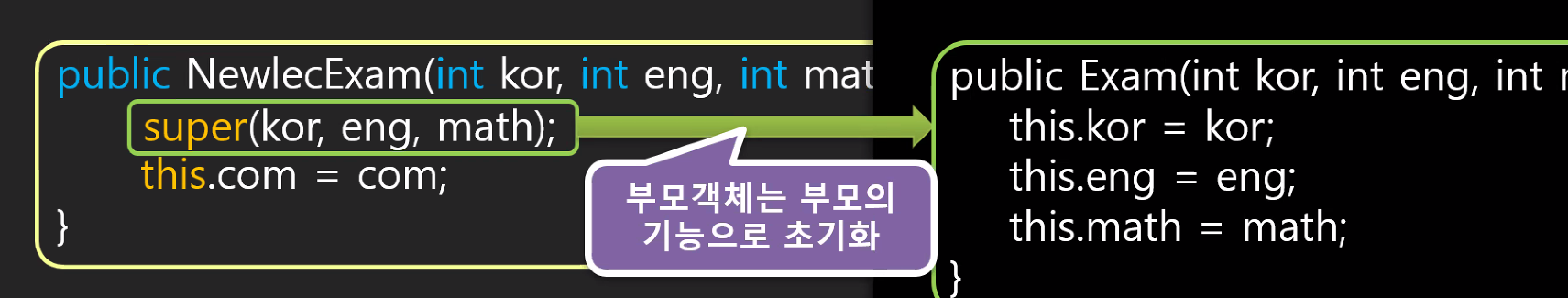
- getter,setter를 쓰기 보다는 super로 하는것이 좋다 (super는 부모의 kor,eng,math를 가져온다는 의미. 그래서 매개인자 쪽에서도 int kor,int eng,int math,int com를 써줬다)
public NewlecExam() {
this(10,10,10,10);
}
public NewlecExam(int kor,int eng,int math,int com) {
super(kor,eng,math);
this.com = com;
}
- 기본생성자에서는 디폴트로 부모생성자를 호출한다 super()가 알아서 생김. 눈에는 보이지 않지만
public int total() {
return super.total()+com;
}
- total이 부모에도 있고 자식에도 있어서 super로 구분을 해줘야 한다

- 참조하고자 하는 내용이 그 객체 안에 있으면 된다
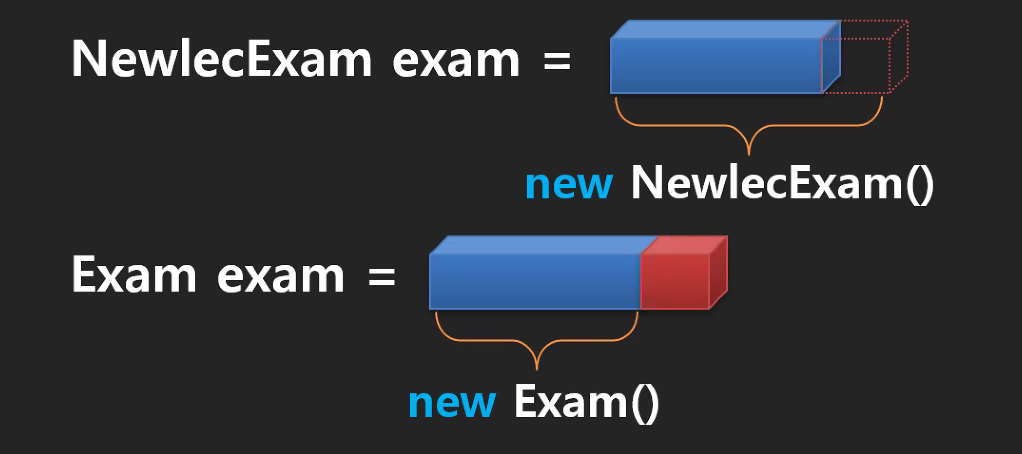

- 부모의 것을 갖고 있으면서 재정의 하는 메서드 > 오버라이드 메서드
- 자바는 모두 앞에 4바이트를 갖고 있다
- 함수정의??를 하지 않으면 부모의 주솟값을 갖게 된다.
- 모든 함수는 동적바인딩으로 이루어진다 > 실행과 동시에
- 앞에 참조형식은 사용할수 있는 함수의 범위를 나타낸다 ex) Exam exam
- 함수의범위를 넘어서 인자를 사용하고싶다면 형변환을 해야한다
ex) A객체에는 없는 B의 객체의 인자를 A객체가 호출한다고 했을때만 형변환 ((B)a).f6();
<오늘 수업 코드 정리...못알아보겠지만 데이터니까..ㅎ>
package ex08.oop.constructor;
public class Exam {
private int kor;
private int eng;
private int math;
public Exam() {
// kor = 2;
// eng = 1;
this(20,20,20); //Exam()이 아닌 public Exam(int kor, int eng, int math) 생성자 호출하면서 초기화
}
public Exam(int kor, int eng, int math) {
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
}
public int getKor() {
return kor;//this.
}
public int getEng() {
return eng;//this.
}
public int getMath() {
return math;//this.
}
public void setKor(int input) {
kor = input;//this.
}
public void setEng(int input) {
eng = input;//this.
}
public void setMath(int input) {
math = input;//this.
}
public int total() {
return kor+eng+math;//this.
}
public int total(int kor, int eng, int math) {
return kor+eng+math;//this.
}
public double avg() {
return total()/3.0;
}
}package ex08.oop.constructor;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExamConsole {
private Exam exam;
public ExamConsole() {
exam = new Exam();
//exam이 콘솔역할을 하게..
}
public void setExam(Exam exam) {
this.exam = exam;
}
public void input() {
// 해당 객체가 상위 클래스에서 실질적으로 존재할 시
//this 생략가능
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("국어 성적을 입력하세요 : ");
int kor = sc.nextInt();//this.
System.out.print("영어 성적을 입력하세요 : ");
int eng = sc.nextInt();//this.
System.out.print("수학 성적을 입력하세요 : ");
int math = sc.nextInt();//this.
exam.setKor(kor);
exam.setEng(eng);
exam.setMath(math);
}
public void print(int num) {
// int total = total();
//
// System.out.printf("국어 %d: %3d 점 \n", num, kor);
// System.out.printf("영어 %d: %3d 점 \n", num, eng);
// System.out.printf("수학 %d: %3d 점 \n", num, math);
// System.out.printf("총점 %d: %3d 점 \n", num, total);
// System.out.println("----------------");
}
}public class NewlecExam extends Exam {
private int com;
public NewlecExam() {
this(10,10,10,10);
}
public NewlecExam(int kor,int eng,int math,int com) {
super(kor,eng,math);
this.com = com;
}
public int getCom() {
return com;
}
public void setCom(int com) {
this.com=com;
}
@Override
public int total() {
return super.total()+com;
//부모의(super) total을 가져와서 이곳에 있는 com까지 더해준 뒤에 total로 반환한다
}package ex08.oop.constructor;
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewlecExam exam = new NewlecExam(10,10,10,10);
System.out.println(exam.total());
//오버라이드된 total이 출력
System.out.println(exam.avg());
}
}